
September 24, 2024 | 19 minute read
The ultimate showdown: MPLS vs. the Internet
Organizations are racing to find faster, cheaper, and more agile ways to connect their global operations, tap into game-changing technologies, and beat the competition. Which has exposed the limitations of many legacy infrastructures, including MPLS. While the MPLS market might be worth USD 68.87 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 92.13 billion by 2029, Internet-based options are closing the gap. For many organizations considering their connectivity strategy, it's MPLS vs. the Internet.
In a world where it’s compete or be outcompeted, ensuring your network connectivity is agile, flexible and resilient enough to get you there is vital, and Internet-based options are winning the race.
If you're a technology leader still using MPLS, understanding its abilities and limitations is crucial. Exploring MPLS replacement, complementary, or hybrid options will ensure your network is ready for transformative technologies.
So keep reading for the ultimate showdown between MPLS and Internet-based WANs.
Firstly, what is MPLS?
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), sometimes even called or even MPLS WAN (Multiprotocol Label Switching Wide Area Network) is a type of data-carrying technique for high-performance telecommunications networks. It is a layer 2 communication switching protocol that relies on compact switching labels to relay payload to the next hop, as opposed to the layer 3 IP addressing used in common IP-routing protocol.
An MPLS Wide Area Network was a great option for a long time due to its ability to prioritize and route data efficiently. It ensured that packets of data take the most efficient route to their destination.
A brief history of MPLS
MPLS WAN networks were developed in the late 1990s as a solution to some of the inefficiencies and scalability issues associated with traditional IP routing. At that time, the growing use of the Internet and the expansion of enterprise networks were putting significant strain on existing networking technologies. MPLS emerged as a more efficient and flexible way to manage traffic, particularly for large organizations with complex networking needs.
In the early 2000s, MPLS became the standard for enterprise networking, especially for organizations with multiple locations spread across geographical areas. By pre-determining each data packet’s route across the network (in a sense, bringing the older telephony model of fixed circuits to the wild world of IP), it gave a range of existing data protocols, like ATM and Frame Relay, the reliability of a fixed-line over a shared network.
How does MPLS work?
MPLS works by assigning labels to those packets of data. These labels are used to create predetermined pathways across the network, called Label-Switched Paths (LSPs).
Unlike traditional IP routing, which involves routing decisions at every hop, MPLS makes routing decisions only once, at the network entry point. This reduces the amount of time it takes for data to travel through the network. Ultimately, leading to a fast and reliable service.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how MPLS works:
- Labeling: When data enters the MPLS network, it is assigned a label that corresponds to a specific path.
- Forwarding: As the data moves through the network, routers use these labels to forward packets along predefined paths.
- Decapsulation: Upon reaching its destination, the label is removed, and the data is forwarded to its final destination using standard IP routing.
MPLS was great for the way this process created efficient data transport, especially over complex, multi-site networks. So really great for global organizations!
So why are businesses moving away from MPLS?
While MPLS has been a reliable and effective networking solution for many years, Omdia expects nearly 40% of enterprise MPLS revenue to be reallocated to other budget priorities over the next five years.
MPLS was the top choice for a long time as network managers appreciated the simplicity of fewer hops and handoffs. However, there are several factors driving businesses to consider MPLS alternatives today:
- Cost: MPLS is expensive, particularly for global organizations that need to maintain multiple MPLS circuits across various locations. However, the cost of deploying and maintaining an MPLS network for smaller businesses can also be a challenge, especially as IT budgets are typically tighter.
- Scalability: Adding new locations or increasing bandwidth requires significant investment in infrastructure and often involves lengthy provisioning times.
- Flexibility: MPLS networks are typically static, with predefined paths that are difficult to change. Which is not very useful given that organizations – and their networks - need to be able to adapt to changing needs quickly.
- Cloud adoption: MPLS is not well-suited for connecting to cloud services, which often require direct Internet access rather than routing traffic through a central data center.
For a full list of the reasons enterprises are moving away from MPLS, check out our article here.
Uncovering the long-term costs of MPLS
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) invested a lot in MPLS. They often will still try and sell it to enterprises even when it might not be best for the customer. Working with the right partner will mean your cost considerations and long-term business goals are taken into account when building, optimizing or maintaining your networks.
MPLS is not only expensive to implement and manage, it also comes with significant long-term costs. Many organizations find themselves in a catch-22 situation of facing the long-term costs of their MPLS investments, and not being able to move away from them to more cost-effective solutions or risk invalidating the money already spent.
That’s why It’s important to truly understand the long-term cost implications of MPLS.
These include:
- Maintenance costs: MPLS networks require ongoing maintenance, including hardware upgrades, software updates, and regular monitoring to ensure optimal performance. These costs can add up over time, particularly for large organizations with complex networks.
- Operational costs: Managing an MPLS network often requires specialized IT staff with expertise in network management and troubleshooting. That means you’re juggling recruitment and retention costs on top of maintenance and equipment costs.
- Opportunity costs: By investing heavily in MPLS, organizations may be reluctant to upgrade their networks to a more flexible solution. This could have long-term impacts on missed opportunity costs if your company can’t adapt to changing business needs and take advantage of new technologies.
- Vendor lock-in: MPLS contracts often involve long-term commitments to a single service provider, which can limit an organization’s ability to switch to a more competitive or innovative solution in the future.
For more insights about the long-term costs impacts, and what some call the “sunken cost fallacy” of MPLS, check out our article here.
What are the MPLS alternatives?
Technology evolves. Business evolves. The market evolves.
And an organization’s network has to evolve to meet these changes. That’s why many Internet-based alternatives to MPLS have emerged to provide the greater flexibility, agility and resilience global enterprises need.
When considering MPLS vs. the Internet, your Internet-based options are:
- SD-WAN: Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) is a popular alternative to MPLS that offers greater flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. In a nutshell, SD-WAN uses software to manage network traffic and can route data over multiple types of connections, including broadband Internet, 4G/5G, and MPLS.
- Direct Internet Access (DIA): DIA provides a dedicated connection to the Internet, offering high-speed, reliable access without the need for an MPLS network. This option, along with SD-WAN, is particularly attractive for organizations that have invested heavily in cloud services.
- VPNs: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) can provide secure, encrypted connections over the public Internet, offering an affordable alternative to MPLS for businesses with less demanding networking needs.
- Hybrid networks: Some organizations are opting for a hybrid approach that combines MPLS with other networking solutions, such as SD-WAN or DIA. This allows them to retain the benefits of MPLS for critical applications while taking advantage of more cost-effective options for less demanding traffic.
It’s important to note at this stage that making the decision between MPLS and an Internet-based alternative can be challenging, but working with a good Managed Service Provider can help you decide which of these options would be the best route forward for your business.
A deep dive: SD-WAN vs. MPLS
Out of the options listed in the above section, SD-WAN has emerged as a strong Internet-based competitor to MPLS. In fact, 79% of organizations currently use SD-WAN solutions, and that number is expected to rise to 92% by 2026.
According to the Expereo-commissioned IDC InfoBrief, Enterprise Horizons 2024: Technology Leaders’ Priorities on their Digital Business Journey, 35% of technology leaders will prioritize SD-WAN solutions implementation above other transformational technologies in terms of financial investment in the next 12 months.
This is unsurprising on many levels as SD-WAN as a networking solution offers several key advantages, including:
- Cost optimizations: SD-WAN is generally more affordable than MPLS, as it can use lower-cost broadband connections instead of expensive MPLS circuits.
- Flexibility: SD-WAN is highly flexible, allowing organizations to easily add new locations, increase bandwidth, and change network configurations without the need for significant infrastructure investments.
- Cloud readiness: SD-WAN is better suited for cloud-based applications as it can route traffic directly to the cloud without the need to backhaul through a central data center.
- Performance optimization: SD-WAN can optimize network performance by dynamically routing traffic over the best available connection, ensuring reliable and consistent service.
The importance of SD-WAN for companies who have chosen a cloud-first strategy cannot be understated. SD-WAN optimizes the use of multiple connections and ensures reliable, high-speed access to cloud services.
And don’t forget, with the cloud you can unlock the potential offered by AI, Machine Learning, Big Data, security and cybersecurity, customer facing applications, etc. And you need SD-WAN to enable your cloud strategy – it truly is a transformation enabler for your network.
Click here to explore our framework for assessing whether your network is cloud-ready.
Exploring software-defined networking
SD-WAN is a software-defined approach to managing wide area networks that is gaining popularity among multi-national organizations. It abstracts the control layer from the hardware, providing centralized and intelligent software-based control. Unlike conventional WANs, which typically rely on expensive hardware-based routers and complex configurations at each location, SD-WAN leverages a software-centric architecture that decouples the network control functions from the underlying physical infrastructure.
This abstraction allows network administrators to manage and optimize traffic flows across the entire network from a single, centralized controller. By using policies defined by the software, SD-WAN dynamically routes traffic over the most efficient and appropriate path. This can be based on real-time conditions such as latency, jitter, or packet loss.
This ability to adapt “on the fly” and the granular control over traffic management means it has application-aware routing. This feature enables the network to prioritize and optimize specific applications. This ensures that business-critical services such as VoIP (Voice over IP), video conferencing, and cloud-based applications receive the necessary bandwidth and low-latency connections to function efficiently.
It's a particularly popular solution for companies prioritizing cloud-first strategies. The Expereo commissioned IDC InfoBrief, Enterprise Horizons 2024: Technology Leaders’ Priorities on their Digital Business Journey showed that 75% of technology leaders feel that cloud connectivity will be very to extremely important in helping their organization achieve its goals. For those companies, SD-WAN provides optimized and secure connectivity to cloud services by intelligently routing traffic directly to the cloud, rather than through a data center.
For more information on the benefits of cloud strategies, check out this thought leadership article.
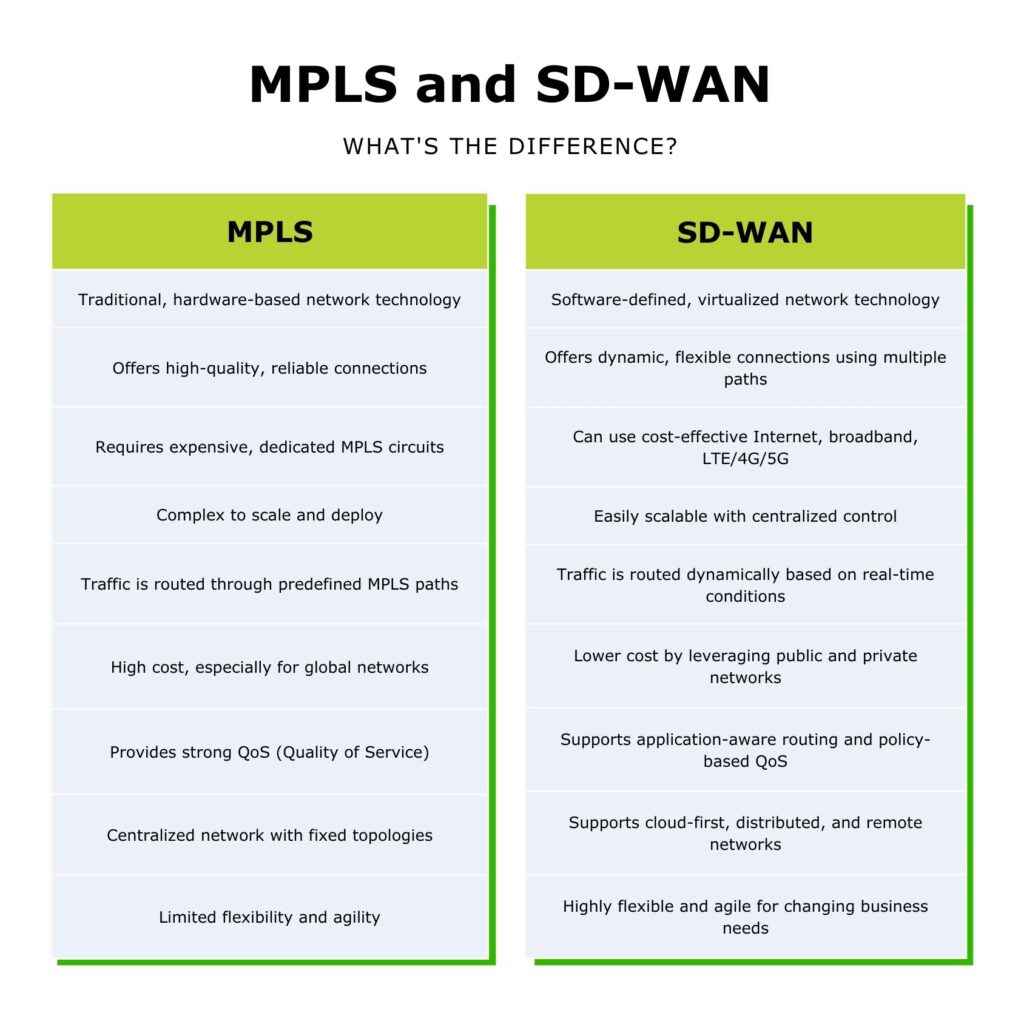
The difference between MPLS and SD-WAN
In some ways, you can consider MPLS to be the like SD-WAN’s forerunner. MPLS applies Quality of Service (QoS) to data packets over different connection types, protocols and even broad geographic areas.
However, there are several other differences between MPLS and SD-WAN you should know about, including:
Architecture:
- MPLS is a hardware-based solution that relies on dedicated circuits and specialized routers. Creating a more rigid and static network infrastructure.
- SD-WAN is a software-based solution that can operate on any standard hardware. Offering a more virtualized and agile approach to network management.
Cost:
- MPLS is typically more expensive due to the need for dedicated infrastructure. This includes leased lines and long-term contracts with service providers.
- SD-WAN is generally more cost-effective. It leverages lower-cost broadband, LTE/4G/5G, and Global Internet connections, reducing dependency on costly MPLS circuits.
Flexibility:
- SD-WAN provides more flexibility compared to MPLS. Organizations can easily add new locations, increase bandwidth, or modify network configurations without making major infrastructure investments.
- MPLS networks require more complex, manual changes and scaling efforts.
Cloud integration:
- SD-WAN is inherently better suited for cloud-based applications. It can intelligently route traffic directly to cloud services without needing to backhaul through a central data center. This improves performance and reduces latency.
- MPLS often routes cloud traffic through a centralized network, which can introduce inefficiencies and delays.
SD-WAN’s benefits over MPLS
SD-WAN offers several advantages over MPLS, including:
- Ease of implementation: As we’ve mentioned,organizations can seamlessly integrate SD-WAN with a variety of connection types (like broadband Internet, MPLS, LTE/4G, and 5G). This means traffic can be intelligently routed over the most efficient connection available, based on the real-time demands of the network.
- Cost optimizations: SD-WAN can significantly reduce networking costs by allowing organizations to use lower-cost broadband connections instead of expensive MPLS circuits. Many companies who make the switch will see a reduction of about 30% in network-related fees.
- Scalability: SD-WAN is easy to scale, so you can add new locations and increase bandwidth as needed without significant infrastructure investments.
- Flexibility: SD-WAN is more flexible than MPLS, it can efficiently adapt to changing business needs so you can take advantage of new technologies.
- Cloud readiness: SD-WAN is better suited for cloud-based applications, as it can route traffic directly to the cloud.
- Performance optimization: SD-WAN can optimize network performance by dynamically routing traffic over the best available connection. This ensures a reliable and consistent service.
Performance optimization is an interesting part of SD-WAN. If you combine it with a connectivity solution like Enhanced Internet from Expereo, you can ensure reliable global application performance. With SD-WAN prioritizing your cloud traffic to the closest PoP, Enhanced Internet can accelerate that traffic via the best-performing route to where the cloud application is hosted. That means lower latency end-to-end, and increased user performance around the world.
Expereo’s Enhanced Internet PoPs are precisely mapped to the data center footprint of major cloud providers. This maximizes our coverage so we can cater for the use cases and locations that your business needs us to deliver.

Explore our full list of SD-WAN’s advantages and business benefits here.
Does SD-WAN replace MPLS?
SD-WAN can replace MPLS in many cases, but it doesn’t have to. It's actually not always MPLS vs. the Internet! Or is SD-WAN better than MPLS...
Some organizations choose to use SD-WAN alongside MPLS in a hybrid network, leveraging the strengths of both technologies. For example, less critical traffic can be sent over public Internet links. And sensitive or high-priority data can be routed over more secure, low-latency MPLS connections.
That said, SD-WAN has some very strong security protocols built in. They can even be further enhanced with a range of Secure Access Service Edge solutions. SD-WAN secures your data at the edge as it moves between different locations and cloud services. SASE ensures that security policies are uniformly applied, regardless of where users or applications are located, providing a seamless and secure user experience.
With security taken care of, many organizations do choose to completely replace MPLS with SD-WAN. This is typically because SD-WAN's ability to dynamically route traffic across multiple connection types makes it an appealing option for businesses that prioritize flexibility and scalability. By transitioning fully to SD-WAN, organizations can achieve greater control over their network, optimize traffic for cloud-based applications, and simplify the integration of new sites or remote workers.
However, it’s important to note that the decision to replace MPLS with SD-WAN depends on your specific business requirements. Such as the need for high-quality, low-latency connections for mission-critical applications or compliance with stringent security policies. To ensure you get the right networking solution for your business’s specific needs, it’s best to work with a trusted partner like a Managed Service Provider, who can guide your decision making process with insight and experience.
Find out more about what makes a good partner when choosing between an MPLS network vs SD-WAN here.
Hybrid networks explained: How SD-WAN works with MPLS
You can integrate SD-WAN with existing MPLS networks to create a hybrid WAN architecture for the best of both worlds.
Here’s how they can work together:
- Traffic segmentation: SD-WAN can direct different types of traffic over the most appropriate connection. MPLS for mission-critical traffic and broadband Internet for less sensitive data.
- Dynamic path selection: SD-WAN can dynamically choose the best available path for data. This can include MPLS, depending on real-time network conditions.
- Load balancing: By using both MPLS and Internet connections, SD-WAN can distribute traffic load more efficiently. Which can let you avoid congestion and optimize performance.
- Failover: If an MPLS connection fails, SD-WAN can reroute traffic over an Internet connection, ensuring continued service without disruption.
However, running SD-WAN across MPLS can be challenging if SD-WAN isn’t deployed properly. For the best results, we advise you work with an experienced Managed Service Provider, like Expereo.
But keep reading for our guide to creating a hybrid network using MPLS and SD-WAN.
How do you embed SD-WAN on top of MPLS?
Essentially, SD-WAN acts as an overlay for your existing MPLS network. It allows you to enjoy the spoils of broadband without uprooting everything from the ground.
To embed SD-WAN on top of an existing MPLS network, follow these steps:
- Assessment: Evaluate your current MPLS infrastructure and identify which parts of your network can benefit from SD-WAN.
- Integration planning: Plan how SD-WAN will be integrated with your existing MPLS. Consider factors like traffic segmentation, routing, and failover strategies.
- Choosing the right SD-WAN solution: Select an SD-WAN solution that complements your MPLS network. Choose one that offers features like traffic steering, dynamic path selection, and centralized management. At Expereo, our solutions engineers will help you choose a solution based on your short, medium and long-term requirements.
- Implementation: Roll out the SD-WAN solution gradually, starting with non-critical segments to minimize risk.
- Monitoring: Use SD-WAN’s analytics and monitoring tools to observe how it performs in conjunction with MPLS and make adjustments as necessary.
- Optimization: Continually optimize the hybrid network setup to ensure it meets your performance, security, and cost-efficiency goals.
Additional considerations when deploying SD-WAN with MPLS:
A few things you should know about implementing SD-WAN on an MPLS network:
- You’ll still have a data center or hub: SD-WAN can exist at the hub, but when it comes to MPLS architectures, you can’t move the data stack or data center.
- There will always be an MPLS port into the hub: When you have MPLS, there’s always a main protected port into the hub for security. You would only get rid of these private lead lines in favor of an SD-WAN connection if they weren’t really needed in the first place.
- You may need more, not less ports: When it comes to MPLS and SD-WAN, you won’t need a port for each IP address on your hybrid network, but you may have to add ports to cloud connections or Infrastructure of as Service (IaaS) providers (like Salesforce, SAP Hana, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Azure, etc. Unfortunately, MPLS ports are expensive, and slow to provision and scale.
- You need to think about where you allocate bandwidth: Your sites that don’t store critical data can be run across best-effort connections with SD-WAN rather than an MPLS circuit. That means you can shed expensive private lines and choose economical secondary connections for specific types of traffic.
Replacing MPLS with SD-WAN: Expereo’s 6-step guide
While you can have MPLS and SD-WAN at the same time, and can even run SD-WAN as an overlay for MPLS, it’s still a good idea to transition fully to Global Internet network supported SD-WAN once your MPLS contract comes up for renewal. This is because MPLS is costly to run, hard to scale, and generally not very flexible or agile.
Transitioning from MPLS to SD-WAN, with the right partner, can be a fast process with minimal disruption.
You’re facing very little downtime, which can cost you a lot on many levels. New locations can be brought online by simply provisioning a new edge device or virtual instance. It will automatically connect to the centralized controller. And configuration updates can be pushed remotely, reducing the need for on-site technical staff.
Best practice for transitioning to SD-WAN:
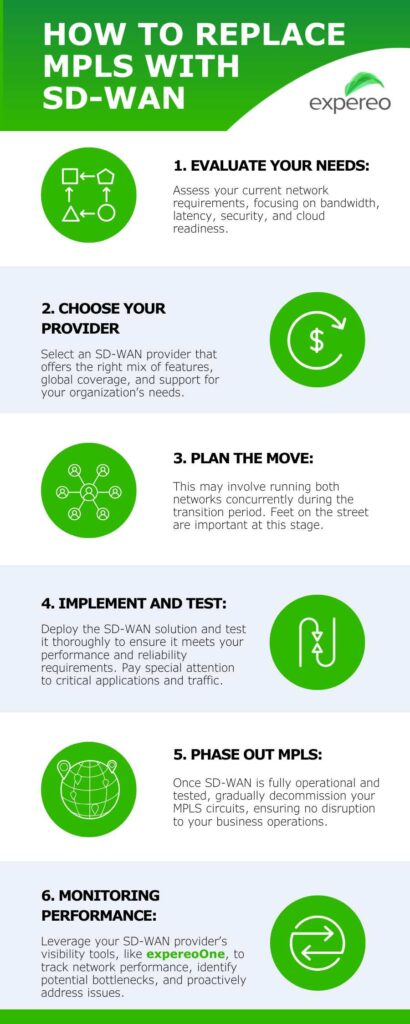
For businesses ready to transition from MPLS to SD-WAN, here is a step-by-step guide that incorporates our best-practice strategies:
- Evaluate your needs: Assess your current network requirements, focusing on bandwidth, latency, security, and cloud readiness.
- Choose the right SD-WAN provider and evaluate logistics: Select an SD-WAN provider that offers the right mix of features, global coverage, and support for your organization’s needs. Try to choose a provider with global reach as logistics and shipping are often difficult to predict and import laws and taxes can be challenging to navigate. In our experience, the more prepared you are, the less time your SD-WAN transformation will take.
- Plan the transition: Develop a phased migration plan to transition from MPLS to SD-WAN. This may involve running both networks concurrently during the transition period. Feet on the street are important at this stage. You need to be able to dispatch local engineers to help with installation, cabling and other hardware issues. No matter where in the world offices are based. Overall, having a single global organization handle all of these logistics can save a lot of time.
- Implement and test: Deploy the SD-WAN solution and test it thoroughly to ensure it meets your performance and reliability requirements. Pay special attention to critical applications and traffic.
- Decommission MPLS: Once SD-WAN is fully operational and tested, gradually decommission your MPLS circuits. This will limit disruption to your business operations.
- Monitoring and optimization: Leverage your SD-WAN provider’s visibility tools, like expereoOne, to track network performance, identify potential bottlenecks, and proactively address issues. Regularly review traffic patterns and adjust policies to prioritize critical applications.
For more information about why you should move away from MPLS to the Internet, explore our guide.
Should you implement SD-WAN alone or with a Managed Service Provider?
When it comes to managing your network, no matter what industry you’re in or what services you provide, it's complicated on a global scale. Additionally, transformation projects are rarely smooth sailing. And when the cost of downtime is estimated at $9,000 per minute, transforming your network needs expert guidance to ensure that critical business continuity.
That’s why partnering with an experienced Managed Service Provider, like Expereo, for your SD-WAN implementation is so important. Expereo has 20+ years of Internet experience. We can help you build a networking strategy that’s fit for purpose now and in the future. So you're free from the constraints of legacy infrastructure.
With Expereo, we also help you manage your SD-WAN network after deployment. This service brings together our technical expertise with our best-in-class technology. Plus, with expereoOne , you can manage your SD-WAN infrastructure alongside the rest of your network in one place. That means full visibility of your services, locations, users and more.

Ready to say goodbye to MPLS?
Ultimately, in the showdown between MPLS vs. the Internet, the decision between MPLS and Internet-based alternatives depends on your organization’s specific needs. While MPLS has long been the go-to solution for reliable, secure networking, the growing demands of digital transformation, cloud adoption, and cost-efficiency are making SD-WAN an increasingly attractive option.
Get in touch with Expereo today to discuss your needs. We’ll help you design, build and run a network that’s purpose-built for your needs. Allowing you to go faster to the future.
Share to
Stay connected with Expereo
Be the first to hear about our latest insights, news, and updates.